ex-USS New Jersey
Ship Stats
Depth: 320 feet
Vessel Type: United States Navy Virginia-class Battleship
Length: 441 feet Breadth: 76.3 feet
Gross Tonnage: 14,948 Cargo: N/A - warship
Built: 1906, Fore River Shipbuilding Co., Quincy, Massachusetts
Owner:United States War Department (1923), formerly United States Navy
Date Lost: September 5, 1923
Sunk By:United States Army Air Service Martin NBS-1 bombers during General Billy Mitchell's aerial bombing tests
Survivors: Unmanned during sinking
Data Collected on Site: Multibeam sonar
Significance: The ex-USS New Jersey participated in the Great White Fleet's around-the-world cruise from 1907 to 1909. The journey, ordered by President Theodore Roosevelt, was to showcase American goodwill and to demonstrate both at home and on the world stage that the United States had become a major sea power. New Jersey and its sister ship, ex-USS Virginia, were both sunk in 1923 during aerial bombing tests conducted by General Billy Mitchell to demonstrate the value of naval air power against capital ships.
Wreck Site
The wreck of the battleship New Jersey lies upside down in 320 feet of water. Multibeam sonar data has been collected at the site, and the inverted hull appears completely intact with a large scour at the bow.

Historical Background
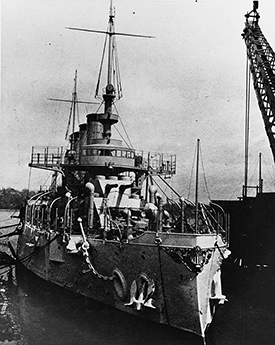
ex-USS New Jersey (BB-16), a 14,948-ton Virginia-class battleship, was built at Quincy, Massachusetts, and commissioned in May 1906, and spent its entire career in the Atlantic Fleet. From December 1907 to February 1909, New Jersey completed a multi-year journey as part of President Roosevelt's "Great White Fleet,” which cruised around the world to demonstrate the United States' contemporary battle fleet and its strategic mobility and power.
After the world cruise, New Jersey was modernized. Painted grey and outfitted with the new "cage" masts, New Jersey operated in the western Atlantic and the Caribbean. In 1914, the vessel took part in the Vera Cruz intervention during the Mexican Revolution. During World War I, New Jersey joined other older battleships in providing shipboard training for the huge numbers of men who joined the wartime Navy. After the war, it made four trans-Atlantic voyages to bring veterans home from Europe. ex-USS New Jersey was decommissioned in August 1920.
Following decommissioning, New Jersey, along with its sister battleship Virginia and the older battleship Alabama, was allocated for weapons tests to be conducted by the U.S. Army Air Service, under the supervision of General Billy Mitchell. On September 5, 1923, Martin NBS-1 bombers from the 2nd Bombardment Group began bombing tests on the New Jersey. The tests occurred in the Atlantic Ocean off Diamond Shoals, North Carolina, with observers aboard the Army transport ship St. Mihiel.
Four of the NBS-1s attacked New Jersey with 600-pound (270 kg) bombs at an altitude of 10,000 feet (3,000 m), scoring four hits and several near-misses, which caused significant flooding to the vessel. Another attack was made, this time with 2,000-pound (910 kg) bombs at 6,000 feet (1,800 m), seven of which landed close to the ship. By this time, flooding had increased to the point that the casemate gun ports were submerged. Two more NBS-1s attacked with two 1,100-pound (500 kg) bombs apiece. The first two missed but the third was a direct hit. It caused a large explosion and New Jersey capsized and sank 24 minutes later. This final service of the ex-USS New Jersey may have been its most valuable.





