ex-USS Virginia
Ship Stats
Depth: 385 feet
Vessel Type: United States Navy Virginia-class battleship
Length: 441 feet Breadth: 76.3 feet
Gross Tonnage: 14,948 Cargo: N/A - warship
Built: 1906, Newport News Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Co., Newport News,Virginia
Owner: United States War Department (1923), formerly United States Navy
Former Names: N/A
Date Lost: September 5, 1923
Sunk By: United States Army Air Service Martin NBS-1 bombers during General Billy Mitchell's aerial bombing tests
Survivors: Unmanned during sinking
Data Collected on Site: Multibeam sonar
Significance: The ex-USS Virginia, the lead ship of its class, participated in the Great White Fleet's around-the-world cruise from 1907 to 1909. The journey, ordered by President Theodore Roosevelt, was to showcase American goodwill and to demonstrate both at home and on the world stage that the U.S. had become a major sea power. The Virginia and its sister ship the ex-USS New Jersey were both sunk in 1923 during aerial bombing tests conducted by General Billy Mitchell to demonstrate the value of naval air power against capital ships.
Wreck Site
The wreck of the battleship Virginia lies upside down in 385 feet of water. Multibeam sonar data has been collected at the site, and the inverted hull appears completely intact with a large scour at the bow that extends out from the shipwreck site.
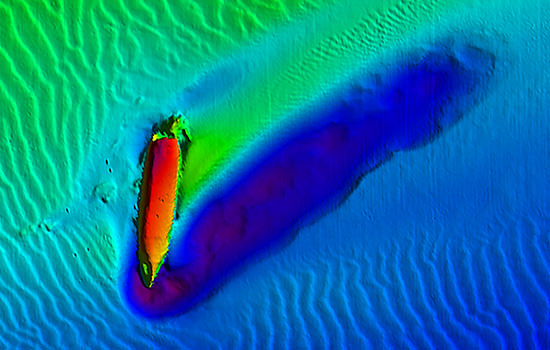
Historical Background

The fourth ship to carry the Virginia name, the battleship ex-USS Virginia, was launched on April 5, 1906, and was sponsored by Miss Gay Montague, daughter of the Governor of Virginia. It was commissioned on May 7, 1906 with Captain Seaton Schroeder in command.
For most of its early career, the Virginia operated along the United States' East Coast with deployments to Cuba in support of the Cuban government as revolution loomed. Then in December 1907, the Virginia participated in an around-the-world cruise of Atlantic Fleet battleships, known as the "Great White Fleet." The fleet of battleships sailed around the world for two years demonstrating the United States' contemporary battle fleet and its strategic mobility and power, returning in February 1909. After the Virginia returned, it went in for an overhaul and spent the next 15 months operating off the Eastern Seaboard. It maintained its routine of operations off the East Coast, occasionally ranging into Cuban waters, until April 1913, when it was sent to Mexico, due to unrest within the country.
While war raged in Europe, the Virginia continued its routine operations, and was placed in reserve in 1916. When the United States entered World War I on April 6, 1917, the government took steps to take over all interned German merchant vessels in American ports. As part of that move, the Virginia sent boarding parties to seize the German passenger and cargo vessels, Amerika, Cincinnati, Wittekind, Koln, and Ockenfels. In early September, the Virginia joined the 3d Division, Battleship Force, Atlantic Fleet and over the next 12 months, first served as a gunnery training ship and later as 1 and 3d Division flagship. After being overhauled in the fall of 1918, the Virginia spent the remainder of the war engaged in convoy escort duties, making only one wartime mission before the armistice was signed on November 11, 1918.
When the war came to an end, troops needed to return home; therefore, a massive troop-lift commenced. The Virginia added additional messing and berthing facilities and conducted five roundtrip voyages to Brest, France, bringing home over 6,000 men. Its last troop lift ended in Boston, on Independence Day 1919.

A year later on August 13, 1920, the Virginia was decommissioned, struck from the Navy list, and then placed up for sale in July 1922. On August 6, 1923, the ship was taken off the sale list and transferred to the War Department for use as a bombing target. Weapons tests were to be conducted by the U.S. Army Air Service, under the supervision of General Billy Mitchell. On September 5, 1923, Martin NBS-1 bombers from the 2nd Bombardment Group began bombing tests on the Virginia and its sister ship, ex-USS New Jersey. The tests occurred in the Atlantic Ocean off Diamond Shoals, North Carolina, with observers aboard the Army transport ship St. Mihiel.
Seven Martins, flying at 3,000 feet, each dropped two 1,100-pound bombs on the Virginia, but only one of them hit. That single bomb completely demolished the ship. An observer later wrote: "Both masts, the bridge, all three smokestacks, and the upper-works disappeared with the explosion and there remained, after the smoke cleared away, nothing but the bare hull, decks blown off, and covered with a mass of tangled debris from stem to stern consisting of stacks, ventilators, cage masts, and bridges."
Within one-half hour of the cataclysmic blast, the Virginia's battered hull sank beneath the waves, and the ex-USS New Jersey joined it shortly. Their sinking provided far-sighted naval officers with a dramatic demonstration of air power and impressed upon them the "urgent need of developing naval aviation with the fleet." As such, the service performed by the old pre-dreadnoughts may have been their most valuable.





